2024

N. R. Olsen; S. M. McKee; O. S. Haddadin; S. M. Lyon; J. E. Campbell; K. K. Leang
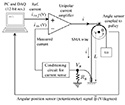
Information-Theoretic Bayesian Inference for Multi-Agent Localization and Tracking of an RF Target with Unknown Waveform Journal Article
In: ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. and Cont., Special Issue on Data-Driven Modeling and Control of Dynamical Systems (https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4066453), vol. 146, iss. 6, pp. 061104, 2024.
@article{OlsenNR_2024_JDSMC,
title = {Information-Theoretic Bayesian Inference for Multi-Agent Localization and Tracking of an RF Target with Unknown Waveform},
author = {N. R. Olsen and S. M. McKee and O. S. Haddadin and S. M. Lyon and J. E. Campbell and K. K. Leang},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/OlsenNR_2024_JDSMC.pdf},
doi = {10.1115/1.4065592},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-08-22},
urldate = {2024-08-22},
journal = {ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. and Cont., Special Issue on Data-Driven Modeling and Control of Dynamical Systems (https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4066453)},
volume = {146},
issue = {6},
pages = {061104},
abstract = {Information-theoretic motion planning and machine learning through Bayesian inference are exploited to localize and track a dynamic radio frequency (RF) emitter with unknown
waveform (uncooperative target). A target-state estimator handles non-Gaussian distributions, while mutual information is utilized to coordinate the motion control of a network of mobile sensors (agents) to minimize measurement uncertainty. The mutual information is computed for pairs of sensors through a four-permutation-with-replacement process. The information surfaces are combined to create a composite map, which is then used by agents to plan their motion for more efficient and effective target estimation and tracking. Simulations and physical experiments involving micro-aerial vehicles with time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurements are performed to evaluate the performance of the algorithm. Results show that when two or three agents are used, the algorithm outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Results also show that for four or more agents, the performance is as competitive as an idealized static sensor network.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
waveform (uncooperative target). A target-state estimator handles non-Gaussian distributions, while mutual information is utilized to coordinate the motion control of a network of mobile sensors (agents) to minimize measurement uncertainty. The mutual information is computed for pairs of sensors through a four-permutation-with-replacement process. The information surfaces are combined to create a composite map, which is then used by agents to plan their motion for more efficient and effective target estimation and tracking. Simulations and physical experiments involving micro-aerial vehicles with time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurements are performed to evaluate the performance of the algorithm. Results show that when two or three agents are used, the algorithm outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Results also show that for four or more agents, the performance is as competitive as an idealized static sensor network.
2023
D. Y. Abramovitch, S. Andersson, K. K. Leang, W. S. Nagel; S. Ruben
A Tutorial on Real-Time Computing Issues for Control Systems Proceedings Article
In: American Control Conference, San Diego, CA, May 31-June 2, 2023.
@inproceedings{AbramovitchDY_2023_ACC,
title = {A Tutorial on Real-Time Computing Issues for Control Systems},
author = {D. Y. Abramovitch, S. Andersson, K. K. Leang, W. S. Nagel and S. Ruben},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-06-02},
urldate = {2023-06-02},
booktitle = {American Control Conference, San Diego, CA, May 31-June 2},
abstract = {This paper presents a tutorial on the elements of computation in a real-time control system. Unlike conventional computation or even computation in digital signal processing systems, computation in a feedback loop must be sensitive to issues of latency and noise around the loop. This presents some fundamental requirements, limitations, and design constraints not seen in other computational applications. The logic of presenting such a tutorial is that while the computer technology changes at a rapid pace, the principles of how we match that technology to the constraints of a feedback loop remain consistent over the years. We will discuss the different computational chains in a feedback system, ways to conceptualize the effects of time delay and jitter on the system, and present a three-layer-model for programming real-time computations. The tutorial also presents some filter and state-space structures that are useful for real-time computation. It concludes with an overview of the different sample rate ranges currently used in some typical control problems and a short discussion of how business models affect our choices in real-time computation.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2022

N. R. Olsen, S. M. McKee, O. S. Haddadin, S. Lyon, J. Campbell, K. K. Leang
Information-Based Mobile Sensor Network Localization and Tracking of an Uncooperative Target Proceedings Article
In: IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), November 28 - December 2, Rockville, MD, USA, pp. 490-495, 2022.
@inproceedings{OlsenNR_2022_MILCOM,
title = {Information-Based Mobile Sensor Network Localization and Tracking of an Uncooperative Target},
author = {N. R. Olsen, S. M. McKee, O. S. Haddadin, S. Lyon, J. Campbell, K. K. Leang},
doi = {10.1109/MILCOM55135.2022.10017826},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-12-02},
urldate = {2022-12-02},
booktitle = {IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), November 28 - December 2, Rockville, MD, USA},
pages = {490-495},
abstract = {This paper focuses on the localization and tracking of a radio frequency (RF) emitter with unknown waveform (uncooperative target) using an information-based centralized network of mobile, collaborative sensors (agents). Each agent utilizes the measured waveform parameters such as time difference of arrival (TDOA), frequency difference of arrival (FDOA), or differential received signal strength (DRSS). The proposed algorithm leverages Bayesian estimation to handle non-Gaussian measurements and it employs information-theoretic motion planning to move sensors to areas of high information-gain to minimize measurement uncertainty. Mutual information is computed for pairs of sensor through a four-permutation with replacement process. The generated mutual information surfaces are combined and then used to plan the motion of each sensor in the network. Simulation results involving TDOA measurements are presented to illustrate the effectiveness of the algorithm, where it is shown that three agents are able to accurately track a target that moves at the same speed as the agents.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
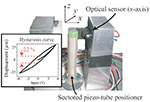
W. S. Nagel, S. Andersson, G. Clayton; K. K. Leang
Low-Coupling Hybrid Parallel-Serial-Kinematic Nanopositioner with Nonorthogonal Flexure: Nonlinear Design and Control Journal Article
In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 27, iss. 5, pp. 3683-3693, 2022.
@article{NagelWS_2022_Tmech,
title = {Low-Coupling Hybrid Parallel-Serial-Kinematic Nanopositioner with Nonorthogonal Flexure: Nonlinear Design and Control},
author = {W. S. Nagel, S. Andersson, G. Clayton and K. K. Leang},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-10-01},
urldate = {2021-11-18},
journal = {IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics},
volume = {27},
issue = {5},
pages = {3683-3693},
abstract = {This article focuses on the design and high-precision control of a new dual-stage, three-axis hybrid parallel-serial-kinematic nanopositioner developed specifically for feature-tracking applications with arbitrary scanning directions. Dual-actuation is achieved by integrating a three-axis shear piezoelectric actuator into the large-range planar stage. A novel nonorthogonal compliant motion-amplifying mechanism which reorients the lateral sample-platform displacement to align with the principal directions of the input piezoactuators is used to minimize parasitic (coupling) motion. A nonlinear rigid-link model and finite element analysis (FEA) are used to optimize over the orientation parameter during the design process. A prototype stage is manufactured and tested, and the lateral and vertical travel ranges are approximately 18 × 21 and 1 μ m, respectively, with secondary lateral actuation in the range of 1 × 1 μ m. Coupling in the long-range stage is below -31 dB for both axes, an estimated 51 to 86% reduction compared to a traditional perpendicular-mechanism design. The measured dominant resonances for the lateral directions of the long-range stage are approximately 1.4 kHz, while short-range positioner resonances are approximately 11 and 40 kHz for the lateral and vertical directions, respectively. The design of a new feedforward-feedback controller is described, and the controller is implemented with field-programmable gate array (FPGA) hardware, where individual actuator contributions are intuitively determined by shaping the frequency response of their relative and summed displacements. An inverse hysteresis operator is used to linearize the plant behavior for effective motion control. Experimental tracking and atomic force microscopy (AFM) imaging results are presented to demonstrate the performance of the new mechanical and control system designs.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
S. M. McKee, O. S. Haddadin; K. K. Leang
Feedforward Mutual-Information Anomaly Detection: Application to Autonomous Vehicles Journal Article
In: ASME Journal of Autonomous Vehicles and Systems, vol. 2, iss. 4, no. 041003 (7 pages), 2022.
@article{McKeeSM_2022_JAVS,
title = {Feedforward Mutual-Information Anomaly Detection: Application to Autonomous Vehicles},
author = {S. M. McKee, O. S. Haddadin and K. K. Leang},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/McKeeSM_2024_JAVS.pdf},
doi = {10.1115/1.4064519},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-10-01},
urldate = {2024-02-13},
journal = {ASME Journal of Autonomous Vehicles and Systems},
volume = {2},
number = {041003 (7 pages)},
issue = {4},
abstract = {This paper describes a mutual-information (MI)-based approach that exploits a dynamics model to quantify and detect anomalies for applications such as autonomous vehicles. First, the MI is utilized to quantify the level of uncertainty associated with the driving behaviors of a vehicle. The MI approach handles novel anomalies without the need for data-intensive training; and the metric readily applies to multivariate datasets for improved robustness compared to, e.g., monitoring vehicle tracking error. Second, to further improve the response time of anomaly detection, current and past measurements are combined with a predictive component that utilizes the vehicle dynamics model. This approach compensates for the lag in the anomaly detection process compared to strictly using current and past measurements. Finally, three different MI-based strategies are described and compared experimentally: anomaly detection using MI with (1) current and past measurements (reaction), (2) current and future information (prediction), and (3) a combination of past and future information (reaction–prediction) with three different time windows. The experiments demonstrate quantification and detection of anomalies in three driving situations: (1) veering off the road, (2) driving on the wrong side of the road, and (3) swerving within a lane. Results show that by anticipating the movements of the vehicle, the quality and response time of the anomaly detection are more favorable for decision-making while not raising false alarms compared to just using current and past measurements.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

M. Goodell
Bayesian Find-and-Consume Strategy for Mobile Robotic Sensor Networks: Estimating and Localizing Multiple Gas Leaks Masters Thesis
2022.
@mastersthesis{GoodellM_2022_MS,
title = {Bayesian Find-and-Consume Strategy for Mobile Robotic Sensor Networks: Estimating and Localizing Multiple Gas Leaks},
author = {M. Goodell},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-05-28},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {mastersthesis}
}

W. S. Nagel
Long-Range Low-Coupling Dual-Stage Nanopositioning: Design and Control for High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy PhD Thesis
2022.
@phdthesis{NagelW_2022_PHD,
title = {Long-Range Low-Coupling Dual-Stage Nanopositioning: Design and Control for High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy},
author = {W. S. Nagel},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-04-18},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
2021

A. Mitrovic, W. S. Nagel, K. K. Leang; G. M. Clayton
Closed-loop Range-Based Control of Dual-Stage Nanopositioning Systems Journal Article
In: IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 26, iss. 3, pp. 1412-1421, 2021.
@article{MitrovicA_2019_TmechSpecialIssue,
title = {Closed-loop Range-Based Control of Dual-Stage Nanopositioning Systems},
author = {A. Mitrovic, W. S. Nagel, K. K. Leang and G. M. Clayton },
doi = {10.1109/TMECH.2020.3020047},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-06-01},
urldate = {2021-06-01},
journal = {IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics},
volume = {26},
issue = {3},
pages = {1412-1421},
abstract = {In this paper, a closed-loop control framework for dual-stage nanopositioning systems is presented that allows the user to allocate control efforts to the individual actuators based on their range capabilities. Recent work by the authors has focused on range-based control of dual-stage actuators implemented as a prefilter, which assumes that each individual actuator has sensor feedback enabling them to be controlled separately. This paper seeks to address the problem of range-based control of dual-stage systems when sensor measurements are only available from the total output of the system, a commonly encountered design. This is a significant departure from previous work since the range-based filter is included in the dual-stage system feedback loop and stability becomes a concern. In this work, the controller is presented, stability conditions are determined, and imaging experiments are performed on an atomic force microscope (AFM). Tracking results show that the root-mean-square (RMS) tracking error for various triangular reference trajectories is improved with the presented range-based control structure by up to 50% compared to frequency-based methods.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
![The American Control Conference [Conference report]](http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/2021_ACCreport.jpg)
S. Devasia, M. Grover; K. K. Leang
The American Control Conference [Conference report] Journal Article
In: IEEE Control Systems Magazine, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 82-86, 2021.
@article{DevasiaS_2021,
title = {The American Control Conference [Conference report]},
author = {S. Devasia, M. Grover and K. K. Leang},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-02-01},
journal = {IEEE Control Systems Magazine},
volume = {41},
number = {1},
pages = {82-86},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2020

J. R. Bourne, M. Goodell, X. He, J. Steiner; K. K. Leang
Decentralized Multi-Agent Information-Theoretic Control for Target Estimation and Localization: Finding Chemical Leaks Journal Article
In: International Journal of Robotics Research, vol. 39, no. 13, pp. 1525 - 1548, 2020.
@article{BourneJR_2020_IJRR,
title = {Decentralized Multi-Agent Information-Theoretic Control for Target Estimation and Localization: Finding Chemical Leaks},
author = {J. R. Bourne, M. Goodell, X. He, J. Steiner and K. K. Leang},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/BourneJR_2020_IJRR.pdf},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1177/0278364920957090},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-07-17},
urldate = {2020-07-17},
journal = {International Journal of Robotics Research},
volume = {39},
number = {13},
pages = {1525 - 1548},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Joseph R. Bourne
Decentralized multi-agent information theoretic target localization and estimation: finding and predicting chemical gas leaks PhD Thesis
University of Utah, 2020.
@phdthesis{BourneJR_2020b,
title = {Decentralized multi-agent information theoretic target localization and estimation: finding and predicting chemical gas leaks},
author = {Joseph R. Bourne},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-06-13},
urldate = {2020-06-13},
school = {University of Utah},
abstract = {The goal of this dissertation is to quickly and autonomously localize and estimate an unknown target, such as a chemical leak, using a team of mobile robots. Accidental or malicious release of chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, or explosive (CBRNE) substances can have devastating effects on humans, animals, infrastructure, and the environment. Thus, fast and accurate localization and estimation of a contaminant release are crucial to saving lives and minimizing damage. To achieve the goal, stochastic estimation and motion planning algorithms are developed, where the performance of two distinct methods for coordinating the mobile robot team are studied. First, a new non-parametric Bayesian-based motion planning algorithm for autonomous plume source term estimation (STE) and source seeking (SS) is developed. Robots coordinate their movements by parsing the belief into multiple modes and they investigate these modes through model-based bio-inspired SS actions. Simulation and experimental results show consistently that the coordinated Bayesian-based STE and SS algorithm outperforms traditional bio-inspired SS and raster-scanning methods, where performance is approximately twice as fast as the uncoordinated case. Second, a new decentralized multi-agent information-theoretic (De-
MAIT) control algorithm that leverages Bayesian estimation and guides robots to minimize uncertainty is developed. The algorithm consists of: (1) a non-parametric Bayesian estimator,
(2) an information-theoretic trajectory planner that generates “informative trajectories” for an agent to follow, and (3) a controller and collision avoidance algorithm that ensure agents follow the trajectory as closely as possible in a safe manner. Simulation results show that the DeMAIT algorithm’s average localization success rate is higher and more robust to changes in the source location, robot team size, and search area size, compared to the coordinated bio-inspired method. Outdoor field experiments are conducted using a team of custom-built aerial robots equipped with gas concentration sensors to estimate and find the source of a propane gas leak to demonstrate efficacy of the DeMAIT algorithm.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
MAIT) control algorithm that leverages Bayesian estimation and guides robots to minimize uncertainty is developed. The algorithm consists of: (1) a non-parametric Bayesian estimator,
(2) an information-theoretic trajectory planner that generates “informative trajectories” for an agent to follow, and (3) a controller and collision avoidance algorithm that ensure agents follow the trajectory as closely as possible in a safe manner. Simulation results show that the DeMAIT algorithm’s average localization success rate is higher and more robust to changes in the source location, robot team size, and search area size, compared to the coordinated bio-inspired method. Outdoor field experiments are conducted using a team of custom-built aerial robots equipped with gas concentration sensors to estimate and find the source of a propane gas leak to demonstrate efficacy of the DeMAIT algorithm.
A. Mitrovic, K. K. Leang; G. M. Clayton
Analysis and Experimental Comparison of Range-based Control for Dual-Stage Nanopositioners Journal Article
In: Mechatronics, Vol. 69, pp. 102371, 2020, 2020.
@article{MitrovicA_2019_Mechatronics,
title = {Analysis and Experimental Comparison of Range-based Control for Dual-Stage Nanopositioners},
author = {A. Mitrovic, K. K. Leang and G. M. Clayton },
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechatronics.2020.102371},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-04-27},
journal = {Mechatronics, Vol. 69, pp. 102371, 2020},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
D. Guo, B. Nagel, G. M. Clayton; K. K. Leang
Spatial-Temporal Trajectory Redesign for Dual-Stage Nanopositioning Systems with Application in AFM Journal Article
In: IEEE/ASME Trans. on Mechatronics, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 558 - 569, 2020.
@article{GuoD_2020_Tmech,
title = {Spatial-Temporal Trajectory Redesign for Dual-Stage Nanopositioning Systems with Application in AFM},
author = {D. Guo, B. Nagel, G. M. Clayton and K. K. Leang},
doi = {10.1109/TMECH.2020.2971755},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-02-25},
journal = {IEEE/ASME Trans. on Mechatronics},
volume = {25},
number = {2},
pages = {558 - 569},
abstract = {This article focuses on trajectory redesign for dual-stage nanopositioning systems, where speed, range, and resolution are considered. Dual-stage nanopositioning systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their unique ability to achieve long-range and high-speed operation. Conventional trajectory assignment methods for dual-stage systems commonly consider frequency characteristics of the actuators, a process that can inappropriately allocate short-range, low-frequency components of a reference signal. A new systematic range-and-temporal-based trajectory-redesign process is presented, where the desired trajectory is first split based on achievable positioning bandwidth, and then, split spatially based on the achievable range and positioning resolution. Inversion-based feedforward control techniques are then used to compensate for the dynamic and hysteretic behaviors of a piezo-based prototype dual-stage positioner; this control architecture is selected to emphasize improvements achieved through the new trajectory-redesign method, as well as allow for implementation onto platforms with minimal sensing capabilities. Simulations and atomic force microscope experiments are included to demonstrate the success of this redesign procedure compared to approaches that consider frequency or range alone.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Xiang He
Modeling and Control of In-Ground-Effect on Rotorcraft Unmanned Aerial Vehicles PhD Thesis
University of Utah, 2020.
@phdthesis{HeX_2020_PhD,
title = {Modeling and Control of In-Ground-Effect on Rotorcraft Unmanned Aerial Vehicles},
author = {Xiang He},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-01-11},
school = {University of Utah},
abstract = {The goal of this dissertation is to model and control the behavior of in-ground-effect (IGE) on multirotor unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Ground effect, or rotor IGE, is a common phenomenon experienced by rotorcraft aerial vehicles when taking off, landing on, hovering around, or flying near surfaces or obstacles. Rotor IGE is caused by aerodynamic interaction between the rotor wake and the nearby obstacle. In particular, the deformed wake causes changes in the induced velocity, which leads to drastic changes in rotor thrust and torque that make flight control in confined spaces difficult and challenging. Many of the existing models for IGE are based on work on helicopters from the early 1940s and more so from the 1950s. Many of these models, unfortunately, are not directly applicable to smaller rotorcraft aerial vehicles due to the assumptions that were made. Also, many of these models suffer from singularities at certain heights, and many of them are computationally heavy. The contributions of this dissertation are computationally-light and accurate models of IGE and the development of feedback controllers that are effective at handling IGE. First, a quasi-steady IGE model for a single rotor that predicts a finite maximum IGE thrust ratio is developed. An empirical approach is used to establish the base exponential function in the quasi-steady model, followed by exploiting blade element theory (BET) and the semipositive induced velocity assumption to relate two IGE model coefficients to blade geometry. The changes in the rotor IGE for various multirotor configurations are studied, characterized, and modeled with respect to the number of rotors, rotor rotation direction, and minimum rotor tip-to-tip distance. The quasi-steady model also incorporates a newly-discovered fountain-vortex thrust loss effect. The quasi-steady model is experimentally validated for off-the-shelf and variable pitch propellers. Second, the quasi-steady model is extended to capture dynamic IGE by considering vehicle flight states and the partial ground effect where a portion of a rotor operates within the ground-effect region. More specifically, using blade element theory, rotor IGE thrust ratios in forward and axial flight are derived as a function of the advance ratio and climbing speed in the IGE regime. A rotation-based IGE test stand that simulates forward flight is created and used to characterize dynamic IGE and to validate the analytical results. The advance ratio, rotor disk angle of attack (AOA), and various multirotor configurations (transverse and tandem rotor) are investigated using the test stand. The partial ground effect is empirically characterized, and the behavior is incorporated into the dynamic IGE model. Finally, the developed IGE models are exploited for vehicle motion control to account for IGE on a quadrotor helicopter (quadcopter) aerial vehicle flying near the ground surface. Specifically, a feedback-based nonlinear disturbance observer controller and a feedforward IGE compensator are designed, simulated, and implemented. Simulation and experimental results validate the effectiveness of the IGE model and flight controller to compensate for IGE when flying close to the ground.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
2019

Dejun Guo
Dynamic and Aggressive Image-Based Flying in GPS-Denied Environments: Estimation, Motion Planning, and Control PhD Thesis
University of Utah, 2019.
@phdthesis{GuoD_2019_PhD,
title = {Dynamic and Aggressive Image-Based Flying in GPS-Denied Environments: Estimation, Motion Planning, and Control},
author = {Dejun Guo},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-05-18},
school = {University of Utah},
abstract = {The goal of this dissertation is to enable an aerial robotic system (including an aircraft with a cable-suspended payload) to fly autonomously in GPS-denied environments through vision from a single monocular camera. To achieve this goal, new estimation, motion planning, and control algorithms that exploit the image-based visual-servo framework are developed. Rigorous stability analysis based on the Lyapunov approach is also presented for the developed control systems. The image-based framework is of interest because of its robustness to image noise and lower computational demand compared to position-based techniques where pose estimation is required. However, this research tackles inherent challenges including nonlinear dynamics, singularity issues, and complex stability analysis for cases with relaxed constraints on initial estimation errors, vehicle position, and height. The resulting theoretical outcomes are validated experimentally by showing demonstrations of aerial-robot assisted operations related to emergency response, search and rescue, and package delivery in GPS-denied environments, such inside of buildings or in urban canyons where global vehicle localization and control schemes are ineffective or impractical. Firstly, a new kinematic image-based control algorithm using a mobile overhead camera for aerial robots is developed. The control algorithm exploits adaptation to compensate for uncertainties in the camera parameters and depth information, and repetitive control is used to reject inherent periodic tracking errors in the image plane. Stability analysis in the Lyapunov sense is shown. Both simulations and physical experiments are provided for a quadcopter to demonstrate the approach. Secondly, a new nonlinear flight control scheme that combines a vision-based closed-loop observer with a backstepping-based controller using an onboard camera and the inertial measurement unit (IMU) is developed. This new approach is computationally efficient and asymptotically stable. Flight tests are conducted to validate the algorithm’s capabilities for take-off, to hover, to track trajectory, and landing. Finally, a new flight control scheme that combines an image-based position controller and a quaternion-based attitude controller are created that enables and aerial robot to fly aggressively through several narrow windows without knowledge of the robot's position and window size, and the approach is extended to control the motion of a cable-suspended payload for package delivery. Both simulations and physical experiments demonstrate that the approaches are capable of flying into and out of a small house and picking up and transporting several packages with unknown mass.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
2018
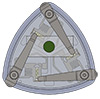
I. Adibnazari, W. S. Nagel; K. K. Leang
A 3D-Printed 3-DOF Tripedal Microrobotic Platform for Unconstrained and Omnidirectional Sample Positioning Journal Article
In: International Journal of Intelligent Robotics and Applications, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 425-435, 2018.
@article{AdibnazariI_2018_IJIRA,
title = {A 3D-Printed 3-DOF Tripedal Microrobotic Platform for Unconstrained and Omnidirectional Sample Positioning},
author = {I. Adibnazari, W. S. Nagel and K. K. Leang},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-11-06},
journal = {International Journal of Intelligent Robotics and Applications},
volume = {2},
number = {4},
pages = {425-435},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Kyle C. Hoffman
Characterization, Modeling, and Feedforward Compensation of Gas Sensor Dynamics for Aerial Robot Chemical Plume Mapping and Swarm-based Localization Masters Thesis
University of Utah, 2018.
@mastersthesis{HoffmanKC_2018_MS,
title = {Characterization, Modeling, and Feedforward Compensation of Gas Sensor Dynamics for Aerial Robot Chemical Plume Mapping and Swarm-based Localization},
author = {Kyle C. Hoffman},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-07-14},
school = {University of Utah},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {mastersthesis}
}
2017
A. Mitrovic, K. K. Leang; G. M. Clayton
Spatial filter design for dual-stage systems Proceedings Article
In: ASME Dynamic Systems and Control Conference (DSCC), Tysons Corner, Virginia, USA, October 11-13, 2107 at the Sheraton Tysons Hotel in Tysons Corner, Virginia, 2017.
@inproceedings{Mitrovica_2017_DSCC,
title = {Spatial filter design for dual-stage systems},
author = {A. Mitrovic, K. K. Leang and G. M. Clayton},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-05-16},
booktitle = {ASME Dynamic Systems and Control Conference (DSCC), Tysons Corner, Virginia, USA, October 11-13, 2107 at the Sheraton Tysons Hotel in Tysons Corner, Virginia},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

J. R. Bourne; K. K. Leang
Mutual Information Control for Target Acquisition: A Method to Localize a Gas/Chemical Plume Source Using a Mobile Sensor Proceedings Article
In: ASME Dynamic Systems and Control Conference (DSCC) Tyson Corner, Virginia, USA, October 11-13, 2017, October 11-13, 2107 at the Sheraton Tysons Hotel in Tysons Corner, Virginia, 2017.
@inproceedings{BourneJR_2017b,
title = {Mutual Information Control for Target Acquisition: A Method to Localize a Gas/Chemical Plume Source Using a Mobile Sensor},
author = {J. R. Bourne and K. K. Leang},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-04-21},
booktitle = {ASME Dynamic Systems and Control Conference (DSCC) Tyson Corner, Virginia, USA, October 11-13, 2017, October 11-13, 2107 at the Sheraton Tysons Hotel in Tysons Corner, Virginia},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2016

Daman Bareiss, Jur van den Berg, Jake Abbott, Kam K. Leang
Study of Improved Pilot Performance using Automatic Collision Avoidance for Tele-operated Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Proceedings Article
In: 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security and Rescue Robotics, October 23-27, 2016, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2016.
@inproceedings{BareissD_2016c,
title = {Study of Improved Pilot Performance using Automatic Collision Avoidance for Tele-operated Unmanned Aerial Vehicles},
author = {Daman Bareiss, Jur van den Berg, Jake Abbott, Kam K. Leang},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/BareissD_2016SSRR.pdf},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-08-23},
booktitle = {2016 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security and Rescue Robotics, October 23-27, 2016, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

D. Bareiss
University of Utah, 2016.
@phdthesis{BareissD_2016b,
title = {Model-based collision avoidance for dynamic single- and multi-robot systems: theory and application in ground and aerial robots},
author = {D. Bareiss},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/2016BareissDissertation.pdf},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-06-07},
school = {University of Utah},
abstract = {This dissertation solves the collision avoidance problem for single and multi-robot systems where dynamic effects are significant. In many robotic systems (e.g., highly maneuverable and agile unmanned aerial vehicles) the dynamics cannot be ignored and collision avoidance schemes based on kinematic models can result in collisions or provide limited performance, especially at high operating speeds. Herein, real-time, model-based collision avoidance algorithms that explicitly consider the robots' dynamics and perform real-time input changes to alter the trajectory and steer the robot away from potential collisions are developed, implemented, and verified in simulations and physical experiments. Such algorithms are critical in applications where a high degree of autonomy and performance are needed, for example in robot-assisted first response where aerial and/or mobile ground robots are required to maneuver quickly through cluttered and dangerous environments in search of survivors. Firstly, the research extends reciprocal collision avoidance to robots with dynamics by unifying previous approaches to reciprocal collision avoidance under a single, generalized representation using control obstacles. In fact, it is shown how velocity obstacles, acceleration velocity obstacles, continuous control obstacles, and linear quadratic regulator (LQR)-obstacles are special instances of the generalized framework. Furthermore, an extension of control obstacles to general reciprocal collision avoidance for non-linear,
non-homogeneous systems where the robots may have different state spaces and different non-linear equations of motion from one another is described. Both simulations and physical experiments are provided for a combination of differential-drive, differential-drive with a trailer, and car-like robots to demonstrate that the approach is capable of letting a non-homogeneous group of robots with non-linear equations of motion safely avoid collisions at real-time computation rates. Secondly, the research develops a stochastic collision avoidance algorithm for a tele-operated unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that considers uncertainty in the robot's dynamics model and the obstacles' position as measured from sensors. The model-based automatic collision avoidance algorithm is implemented on a custom-designed quadcopter UAV system with on-board computation and the sensor data is processed using a split-and-merge segmentation algorithm and an approximate Minkowski difference. Flight tests are conducted to validate the algorithm's capabilities for providing tele-operated collision-free operation. Finally, a set of human subject studies are performed to quantitatively compare the performance between the model-based algorithm, the basic risk field algorithm (a variant on potential field), and full manual control. The results show that the model-based algorithm performs significantly better than manual control in both the number of collisions and the UAVs average speed, both of which are extremely vital, for example, for UAV-assisted search and rescue applications. Compared to the potential-field based algorithm, the model-based algorithm allowed the pilot to operate the UAV with higher average speeds.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
non-homogeneous systems where the robots may have different state spaces and different non-linear equations of motion from one another is described. Both simulations and physical experiments are provided for a combination of differential-drive, differential-drive with a trailer, and car-like robots to demonstrate that the approach is capable of letting a non-homogeneous group of robots with non-linear equations of motion safely avoid collisions at real-time computation rates. Secondly, the research develops a stochastic collision avoidance algorithm for a tele-operated unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that considers uncertainty in the robot's dynamics model and the obstacles' position as measured from sensors. The model-based automatic collision avoidance algorithm is implemented on a custom-designed quadcopter UAV system with on-board computation and the sensor data is processed using a split-and-merge segmentation algorithm and an approximate Minkowski difference. Flight tests are conducted to validate the algorithm's capabilities for providing tele-operated collision-free operation. Finally, a set of human subject studies are performed to quantitatively compare the performance between the model-based algorithm, the basic risk field algorithm (a variant on potential field), and full manual control. The results show that the model-based algorithm performs significantly better than manual control in both the number of collisions and the UAVs average speed, both of which are extremely vital, for example, for UAV-assisted search and rescue applications. Compared to the potential-field based algorithm, the model-based algorithm allowed the pilot to operate the UAV with higher average speeds.
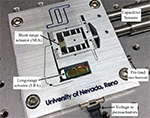
W. S. Nagel, G. M. Clayton; K. K. Leang
Master-slave control with hysteresis inversion for dual-stage nanopositioning systems Proceedings Article
In: American Control Conference (Accepted), Boston MA, July 6-8, 2016, 2016.
@inproceedings{NagelWS_2016a,
title = {Master-slave control with hysteresis inversion for dual-stage nanopositioning systems},
author = {W. S. Nagel, G. M. Clayton and K. K. Leang},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-28},
booktitle = {American Control Conference (Accepted), Boston MA, July 6-8, 2016},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
K. K. Leang; A. J. Fleming
Tracking control for nanopositioning systems, in Fundamentals and Applications of Nanopositioning Technologies Book Chapter
In: Ru, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y. (Ed.): Fundamentals and Applications of Nanopositioning Technologies, Springer, 2016.
@inbook{Leangkk_2016a,
title = {Tracking control for nanopositioning systems, in Fundamentals and Applications of Nanopositioning Technologies},
author = {K. K. Leang and A. J. Fleming},
editor = {C. Ru and X. Liu and Y. Sun},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-01-01},
booktitle = {Fundamentals and Applications of Nanopositioning Technologies},
publisher = {Springer},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
2015
Daman Bareiss, Jur van den Berg; Kam K. Leang
Stochastic automatic collision avoidance for tele-operated unmanned aerial vehicles Proceedings Article
In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), September 28 - October 02, pp. 4818-4825, Hamburg, Germany, 2015.
@inproceedings{BareissDa_2015,
title = {Stochastic automatic collision avoidance for tele-operated unmanned aerial vehicles},
author = {Daman Bareiss, Jur van den Berg and Kam K. Leang},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/BareissD_2015a.pdf},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-07-31},
booktitle = {IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), September 28 - October 02},
pages = {4818-4825},
address = {Hamburg, Germany},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2014

A. J. Fleming; K. K. Leang
Design, modeling, and control of nanopositioning systems Book
Springer, New York, 2014, ISBN: 3319066161.
@book{FlemingAJ_2013d,
title = {Design, modeling, and control of nanopositioning systems},
author = { A. J. Fleming and K. K. Leang},
url = {http://www.amazon.com/Modeling-Control-Nanopositioning-Advances-Industrial/dp/3319066161},
isbn = {3319066161},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-06-03},
publisher = {Springer},
address = {New York},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {book}
}
G. C. Clayton; C. J. Dudley; K. K. Leang
Range-based control of dual-stage nanopositioning systems Journal Article
In: Review of Scientific Instruments, vol. 85, no. 4, pp. 045003 (6 pages), 2014.
@article{ClaytonGC_2014a,
title = {Range-based control of dual-stage nanopositioning systems},
author = { G. C. Clayton and C. J. Dudley and K. K. Leang},
url = {http://kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/ClaytonGM_2014a.pdf},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-04-01},
journal = {Review of Scientific Instruments},
volume = {85},
number = {4},
pages = {045003 (6 pages)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2012

Maxwell J. Fleming
Mitigating IPMC back relaxation through feedforward and feedback control of patterned electrodes Masters Thesis
2012.
@mastersthesis{FlemingMJ_2012a,
title = {Mitigating IPMC back relaxation through feedforward and feedback control of patterned electrodes},
author = {Maxwell J. Fleming},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/FlemingMJ_MSThesis.pdf},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-06-01},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {mastersthesis}
}
G. M. Clayton; K. K. Leang
Spatial-temporal control of dual-stage nanpositioners Proceedings Article
In: IEEE Control and Decision Conference, 2012.
@inproceedings{ClaytonGM_2012a,
title = {Spatial-temporal control of dual-stage nanpositioners},
author = { G. M. Clayton and K. K. Leang},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
booktitle = {IEEE Control and Decision Conference},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Y. Yong; S. O. R. Moheimani; B. J. Kenton; K. K. Leang
Invited Review: High-speed flexure-guided nanopositioning: mechanical design and control Issues Journal Article
In: Review of Scientific Instruments, vol. 83, no. 12, pp. 121101, 2012.
@article{YongY_2012,
title = {Invited Review: High-speed flexure-guided nanopositioning: mechanical design and control Issues},
author = { Y. Yong and S. O. R. Moheimani and B. J. Kenton and K. K. Leang},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/YongYK_2012.pdf},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
journal = {Review of Scientific Instruments},
volume = {83},
number = {12},
pages = {121101},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

B. J. Kenton; K. K. Leang
Design and control of a three-axis serial-kinematic high-bandwidth nanopositioner Journal Article
In: IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 356 – 369, 2012.
@article{KentonBJ_2012,
title = {Design and control of a three-axis serial-kinematic high-bandwidth nanopositioner},
author = { B. J. Kenton and K. K. Leang},
url = {http://kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/KentonBJ_2012a.pdf},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-01-01},
journal = {IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics},
volume = {17},
number = {2},
pages = {356 -- 369},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2011

Yingfeng Shan
Repetitive control for hysteretic systems: theory and application in piezo-based nanopositioners PhD Thesis
Univesity of Nevada, Reno, 2011.
@phdthesis{ShanY_2011b,
title = {Repetitive control for hysteretic systems: theory and application in piezo-based nanopositioners},
author = {Yingfeng Shan},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/ShanY_2011_Dissertation.pdf},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-12-17},
address = {Reno, Nevada 89557-0312},
school = {Univesity of Nevada, Reno},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
M. J. Fleming; K. J. Kim; K. K. Leang
Mitigating IPMC back-relaxation effect using multi-input control Proceedings Article
In: ASME Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems (SMASIS), 2011.
@inproceedings{FlemingM_2011a,
title = {Mitigating IPMC back-relaxation effect using multi-input control},
author = { M. J. Fleming and K. J. Kim and K. K. Leang},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-01-01},
booktitle = {ASME Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems (SMASIS)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2010

Seth C. Ashley
Application of an Inverse-Hysteresis Iterative Control Algorithm for AFM Fabrication Masters Thesis
University of Nevada, Reno, Reno, Nevada, 2010.
@mastersthesis{AshleySC_2010,
title = {Application of an Inverse-Hysteresis Iterative Control Algorithm for AFM Fabrication},
author = {Seth C. Ashley},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/AshleySC_2010_MSThesis.pdf},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-10-23},
address = {Reno, Nevada},
school = {University of Nevada, Reno},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {mastersthesis}
}

Brian J. Kenton
University of Nevada, Reno, Reno, Nevada, 2010.
@mastersthesis{KentonBJ_2010b,
title = {Design, characterization, and control of a high-bandwidth serial-kinematic nanopositioning stage for scanning probe microscopy applications},
author = {Brian J. Kenton},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/BJKentonThesis2010.pdf},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-08-28},
address = {Reno, Nevada},
school = {University of Nevada, Reno},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {mastersthesis}
}

A. J. Fleming; K. K. Leang
Measurement and control for high-speed sub-atomic positioning in scanning probe microscopes Proceedings Article
In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA2010), Invited workshop, May 3-8, 2010.
@inproceedings{FlemingAJ_2010f,
title = {Measurement and control for high-speed sub-atomic positioning in scanning probe microscopes},
author = { A. J. Fleming and K. K. Leang},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-01-01},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA2010), Invited workshop, May 3-8},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
B. J. Kenton; K. K. Leang
Design, characterization, and control of a monolithic three-axis high-bandwidth nanopositioning stage Proceedings Article
In: American Control Conference, Special Invited Session on Advances in Actuation for Nanopositioning and Scanning Probe Systems, pp. 4949 – 4956, 2010.
@inproceedings{KentonBJ_2010a,
title = {Design, characterization, and control of a monolithic three-axis high-bandwidth nanopositioning stage},
author = { B. J. Kenton and K. K. Leang},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-01-01},
booktitle = {American Control Conference, Special Invited Session on Advances in Actuation for Nanopositioning and Scanning Probe Systems},
pages = {4949 -- 4956},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2009
Y. Shan; K. K. Leang
Frequency-weighted feedforward control for dynamic compensation in ionic polymer-metal composite actuators Journal Article
In: Smart Materials and Structures, vol. 18, no. 12, pp. 125016 (11 pages), 2009.
@article{ShanY_2009b,
title = {Frequency-weighted feedforward control for dynamic compensation in ionic polymer-metal composite actuators},
author = { Y. Shan and K. K. Leang},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-01-01},
journal = {Smart Materials and Structures},
volume = {18},
number = {12},
pages = {125016 (11 pages)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

K. K. Leang; Q. Zou; S. Devasia
Feedforward control of piezoactuators in atomic force microscope systems: inversion-based compensation for dynamics and hysteresis Journal Article
In: IEEE Cont. Syst. Mag., Special Issue on Hysteresis, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 70 – 82, 2009.
@article{LeangKK_2009b,
title = {Feedforward control of piezoactuators in atomic force microscope systems: inversion-based compensation for dynamics and hysteresis},
author = { K. K. Leang and Q. Zou and S. Devasia},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-01-01},
journal = {IEEE Cont. Syst. Mag., Special Issue on Hysteresis},
volume = {29},
number = {1},
pages = {70 -- 82},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
G. M. Clayton; S. Tien; K. K. Leang; Q. Zou; S. Devasia
A review of feedforward control approaches in nanopositioning for high speed SPM Journal Article
In: ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. and Cont., vol. 131, no. 6, pp. 061101 (19 pages), 2009.
@article{ClaytonGM_2009,
title = {A review of feedforward control approaches in nanopositioning for high speed SPM},
author = { G. M. Clayton and S. Tien and K. K. Leang and Q. Zou and S. Devasia},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-01-01},
journal = {ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. and Cont.},
volume = {131},
number = {6},
pages = {061101 (19 pages)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
K. K. Leang; S. C. Ashley; G. Tchoupo
Iterative and feedback control for hysteresis compensation in SMA Journal Article
In: ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. and Cont., vol. 131, pp. 014502 (6 pages), 2009.
@article{LeangKK_2009a,
title = {Iterative and feedback control for hysteresis compensation in SMA},
author = { K. K. Leang and S. C. Ashley and G. Tchoupo},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-01-01},
journal = {ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. and Cont.},
volume = {131},
pages = {014502 (6 pages)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2008
S. C. Ashley; U. Aridogan; R. O. Riddle; K. K. Leang
Hysteresis inverse iterative learning control of piezoactuators in AFM Proceedings Article
In: 17th IFAC World Congress, Invited Session on Dynamics and Control of Micro- and Nanoscale Systems, 2008.
@inproceedings{AshleySC_2008,
title = {Hysteresis inverse iterative learning control of piezoactuators in AFM},
author = { S. C. Ashley and U. Aridogan and R. O. Riddle and K. K. Leang},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/AshleySC_2008.pdf},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-01-01},
booktitle = {17th IFAC World Congress, Invited Session on Dynamics and Control of Micro- and Nanoscale Systems},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Y. Shan; K. K. Leang
Application of Feedforward Dynamics Compensation in Ionic-Polymer Metal Composite Actuators Proceedings Article
In: SPIE Smart Structures and Materials and NDE for Health Monitoring and Diagnostics Conference, pp. 69270F-1 – 69270F-12, 2008.
@inproceedings{ShanY_2008,
title = {Application of Feedforward Dynamics Compensation in Ionic-Polymer Metal Composite Actuators},
author = { Y. Shan and K. K. Leang},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-01-01},
booktitle = {SPIE Smart Structures and Materials and NDE for Health Monitoring and Diagnostics Conference},
volume = {6927},
pages = {69270F-1 -- 69270F-12},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

D. Iamratanakul; B. Jordan; K. K. Leang; S. Devasia
Optimal seek-trajectory design for dual-stage systems Journal Article
In: IEEE Trans. Cont. Sys. Tech., vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 869 – 881, 2008.
@article{IamratanakulD_2008,
title = {Optimal seek-trajectory design for dual-stage systems},
author = { D. Iamratanakul and B. Jordan and K. K. Leang and S. Devasia},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-01-01},
journal = {IEEE Trans. Cont. Sys. Tech.},
volume = {16},
number = {5},
pages = {869 -- 881},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2007
G. Tchoupo; K. K. Leang
Hysteresis compensation for high-precision positioning of a shape memory alloy actuator using integrated iterative-feedforward and feedback inputs Proceedings Article
In: American Control Conference, pp. 4246 – 4253, 2007.
@inproceedings{TchoupoG_2007a,
title = {Hysteresis compensation for high-precision positioning of a shape memory alloy actuator using integrated iterative-feedforward and feedback inputs},
author = { G. Tchoupo and K. K. Leang},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
booktitle = {American Control Conference},
pages = {4246 -- 4253},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
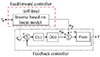
K. K. Leang; S. Devasia
Feedback-linearized inverse feedforward for creep, hysteresis, and vibration compensation in AFM piezoactuators Journal Article
In: IEEE Trans. Cont. Syst. Tech., vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 927 – 935, 2007.
@article{LeangKK_2007,
title = {Feedback-linearized inverse feedforward for creep, hysteresis, and vibration compensation in AFM piezoactuators},
author = {K. K. Leang and S. Devasia},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/LeangKK_2007.pdf},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
journal = {IEEE Trans. Cont. Syst. Tech.},
volume = {15},
number = {5},
pages = {927 -- 935},
abstract = {In this brief, we study the design of a feedback and feedforward controller to compensate for creep, hysteresis, and vibration effects in an experimental piezoactuator system. First, we linearize the nonlinear dynamics of the piezoactuator by accounting for the hysteresis (as well as creep) using high-gain feedback control. Next, we model the linear vibrational dynamics and then invert the model to find a feedforward input to account vibration -- this process is significantly easier than considering the complete nonlinear dynamics (which combines hysteresis and vibration effects). Afterwards, the feedforward input is augmented to the feedback-linearized system to achieve high-precision high-speed positioning. We apply the method to a piezoscanner used in an experimental atomic force microscope to demonstrate the method’s effectiveness and we show significant reduction of both the maximum and root-mean-square tracking error. For example, high-gain feedback control compensates for hysteresis and creep effects, and in our case, it reduces the maximum error (compared to the uncompensated case) by over 90%. Then, at relatively high scan rates, the performance of the feedback controlled system can be improved by over 75% (i.e., reduction of maximum error) when the inversion-based feedforward input is integrated with the high-gain feedback controlled system.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2006
K. K. Leang; S. Devasia
Design of hysteresis-compensating iterative learning control for piezo positioners: application to atomic force microscopes Journal Article
In: Mechatronics, vol. 16, no. 3--4, pp. 141 – 158, 2006.
@article{LeangKK_2006,
title = {Design of hysteresis-compensating iterative learning control for piezo positioners: application to atomic force microscopes},
author = { K. K. Leang and S. Devasia},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-01-01},
journal = {Mechatronics},
volume = {16},
number = {3--4},
pages = {141 -- 158},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
S. C. Ashley; G. Tchoupo; R. M. Mohr; K. K. Leang
Precise positioning of a shape memory alloy actuator using iterative control Proceedings Article
In: Actuator 2006, pp. 467 – 470, 2006.
@inproceedings{AshleySC_2006,
title = {Precise positioning of a shape memory alloy actuator using iterative control},
author = { S. C. Ashley and G. Tchoupo and R. M. Mohr and K. K. Leang},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/AshleySC_2006.pdf},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-01-01},
booktitle = {Actuator 2006},
pages = {467 -- 470},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

D. Iamratanakul; B. Jordan; K. K. Leang; S. Devasia
Optimal seek-trajectory design for dual-stage systems Proceedings Article
In: American Control Conference, pp. 606 – 612, 2006.
@inproceedings{IamratanakulD_2006,
title = {Optimal seek-trajectory design for dual-stage systems},
author = { D. Iamratanakul and B. Jordan and K. K. Leang and S. Devasia},
year = {2006},
date = {2006-01-01},
booktitle = {American Control Conference},
pages = {606 -- 612},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2004
K. K. Leang; S. Devasia
Iterative learning control of piezo positioners for long-range SPM-based nanofabrication Proceedings Article
In: The 3rd IFAC Symposium on Mechatronic Systems, 2004.
@inproceedings{LeangKK_2004a,
title = {Iterative learning control of piezo positioners for long-range SPM-based nanofabrication},
author = { K. K. Leang and S. Devasia},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
booktitle = {The 3rd IFAC Symposium on Mechatronic Systems},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

K. K. Leang
University of Washington, 2004.
@phdthesis{LeangKK_2004b,
title = {Iterative learning control of hysteresis in piezo-based nanopositioners: theory and application in atomic force microscopes},
author = {K. K. Leang},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/KamKLeangPhDDec2004.pdf},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
address = {Seattle, WA},
school = {University of Washington},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
Q. Zou; K. K. Leang; E. Sadoun; M. J. Reed; S. Devasia
Control issues in high-speed AFM for biological applications: collagen imaging example Journal Article
In: Asian Journal of Control, Special issue on Advances in Nanotechnology Control, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 164-178, 2004.
@article{ZouQ_2004,
title = {Control issues in high-speed AFM for biological applications: collagen imaging example},
author = { Q. Zou and K. K. Leang and E. Sadoun and M. J. Reed and S. Devasia},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-01-01},
journal = {Asian Journal of Control, Special issue on Advances in Nanotechnology Control},
volume = {6},
number = {2},
pages = {164-178},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2003
K. K. Leang; S. Devasia
Iterative feedforward compensation of hysteresis in piezo positioners Proceedings Article
In: IEEE 42nd Conference on Decision and Controls, Invited session on Nanotechnology: Control Needs and Related Perspectives, pp. 2626 - 2631, 2003.
@inproceedings{LeangKK_2003,
title = {Iterative feedforward compensation of hysteresis in piezo positioners},
author = { K. K. Leang and S. Devasia},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
booktitle = {IEEE 42nd Conference on Decision and Controls, Invited session on Nanotechnology: Control Needs and Related Perspectives},
pages = {2626 - 2631},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
1998
J. S. Dewey; K. K. Leang; S. Devasia
Experimental and theoretical results in output-trajectory redesign for flexible structures Journal Article
In: ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., and Control, vol. 120, no. 4, pp. 456-461, 1998.
@article{DeweyJS_1998,
title = {Experimental and theoretical results in output-trajectory redesign for flexible structures},
author = { J. S. Dewey and K. K. Leang and S. Devasia},
url = {http://www.kam.k.leang.com/academics/pubs/DeweyJS_1998.pdf},
year = {1998},
date = {1998-01-01},
journal = {ASME J. Dyn. Syst., Meas., and Control},
volume = {120},
number = {4},
pages = {456-461},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}







